UDC-VIT
UDC-VIT는 언더-디스플레이 카메라(UDC) 환경에서 촬영된 세계 최초의 실제 비디오 데이터셋입니다.
본 데이터셋은 다양한 장면, 조명 조건, 움직임을 포함하며, 기존 합성 데이터셋이 충분히 반영하지 못했던 심각한 노이즈, 투과율 저하, 플레어 등 실제 열화 현상을 담고 있습니다.
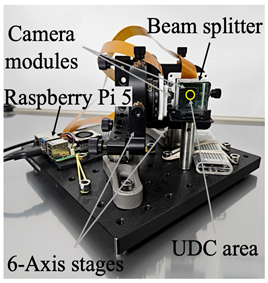
프레임 간 정밀한 정렬 정확도(alignment accuracy)를 확보하기 위해, 빔스플리터를 활용한 비디오 촬영 시스템을 구축하여 고품질 타겟 영상과 UDC 열화 영상을 동시에 수집하였습니다.
수집된 영상 쌍은 이산 푸리에 변환(discrete Fourier transform, DFT)을 활용해 98.95%의 높은 정확도로 정렬되었습니다.
UDC-VIT is the first real-world video dataset captured under under-display camera (UDC) conditions.
It encompasses a diverse range of scenes, lighting conditions, and human motion patterns.
The dataset faithfully captures actual degradations that existing synthetic datasets fail to adequately depict,
such as severe noise, transmittance loss, and variant flare.
To ensure precise alignment accuracy between corresponding frames, we design a video capturing system using a beam splitter, enabling the simultaneous acquisition of high-quality target videos and UDC-degraded videos. Paired frames are aligned with 98.95% accuracy using discrete Fourier transform (DFT)-based methods.
안면 인식 성능 평가를 위해, 서울대학교 생명윤리위원회(Institutional Review Board, IRB)의 심의를 거쳐 22명의 연구참여자를 모집하고 실제 얼굴 영상을 촬영하였습니다.
UDC-VIT은 UDC 비디오 복원 및 안면 인식 연구를 위한 신뢰도 높은 벤치마크를 제공합니다. 특히, UDC-VIT과 기존 합성 데이터셋 간의 미세 조정(fine-tuning) 실험을 통해, 합성 데이터로 학습된 모델이 실제 데이터에 대해 일반화 성능이 제한적임을 확인하였으며, 실제 데이터 기반 연구의 중요성을 뒷받침합니다.
To evaluate face recognition performance, we obtained approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Seoul National University and captured real face videos from 22 recruited participants.
UDC-VIT serves as a reliable benchmark for UDC video restoration and face recognition tasks. Notably, cross-dataset fine-tuning experiments indicate that models trained solely on synthetic data generalize poorly to UDC-VIT, highlighting the importance of real-world datasets for advancing UDC research.
| 데이터셋 이름 | 형태 | 장면 | 데이터셋 개수 | 해상도 | fps | 플레어 존재 여부 | 안면 인식 | 데이터셋 공개 여부 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-OLED/P-OLED | 이미지 | 합성 | 300 | 1024x2048x3 | - | ✓ | ||
| SYNTH | 이미지 | 합성 | 2,376 | 800x800x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Pseudo-real | 이미지 | 실제 | 6,747 | 512x512x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| UDC-SIT | 이미지 | 실제 | 2,340 | 1792x1280x4 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Tan et al. | 이미지 | 합성 | 73,000 | - | - | ✓ | ||
| Wang et al. | 이미지 | 합성 | 56,126 | - | - | ✓ | ||
| PixelsUDC-T/P | 비디오 | 합성 | 160x100 (16,000) |
1280x720x3 | 25-50 | |||
| VidUDC33K | 비디오 | 합성 | 677x50 (33,850) |
1920x1080x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| UDC-VIT | 비디오 | 실제 | 647x180 (116,460) |
1900x1060x3 | 60 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Dataset | Type | Scene | Dataset Size | Resolution | fps | Flare | Face | Publicly Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-OLED/P-OLED | Image | Synthetic | 300 | 1024x2048x3 | - | ✓ | ||
| SYNTH | Image | Synthetic | 2,376 | 800x800x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Pseudo-real | Image | Real | 6,747 | 512x512x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| UDC-SIT | Image | Real | 2,340 | 1792x1280x4 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Tan et al. | Image | Synthetic | 73,000 | - | - | ✓ | ||
| Wang et al. | Image | Synthetic | 56,126 | - | - | ✓ | ||
| PixelsUDC-T/P | Video | Synthetic | 160x100 (16,000) |
1280x720x3 | 25-50 | |||
| VidUDC33K | Video | Synthetic | 677x50 (33,850) |
1920x1080x3 | - | ✓ | ✓ | |
| UDC-VIT | Video | Real | 647x180 (116,460) |
1900x1060x3 | 60 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
✻ 노이즈 및 투과율 감소
✻ Noise and Transmittance Decrease
기존 UDC 합성 비디오 데이터셋은 Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)으로 degradation을 생성하거나 다음과 같은 수식으로 degradation을 생성합니다:
Existing UDC synthetic video datasets generate degradations using Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) or based on the following formulation:
\( I_D^t=f(\gamma\cdot I_G^t \times k_t +n) \)
여기서 \(I_D^t\)와 \(I_G^t\)는 각각 UDC 열화 영상과 타겟 영상, \(\gamma\)는 강도 조절 인자(intensity scaling factor), \(k_t\)는 회절 커널(point spread function, PSF), \(n\)은 노이즈, \(f\)는 픽셀 값 포화(clamp) 함수입니다. 이 수식에 기반한 방식은 noise 및 투과율 저하를 모사하지만, 실제 환경에서 관찰되는 복잡한 noise 특성과 투과율 감소를 완벽히 재현하지 못합니다. 반면, UDC-VIT는 Samsung Galaxy Z-Fold 5의 카메라와 동일하게 Quad-Bayer Coding(QBC) 카메라 모듈을 사용하여 실제 noise 및 투과율 저하를 더 정확하게 모사합니다.
where \(I_D^t\) and \(I_G^t\) denote the UDC-degraded and ground-truth frames, respectively. \(\gamma\) is the intensity scaling factor, \(k_t\) refers to the diffraction kernel (i.e., PSF), \(n\) is the noise, and \(f\) denotes the clamp function for the pixel value saturation. Although this model simulates noise and transmittance loss, it fails to fully reproduce the complex noise characteristics and transmittance degradation observed in real-world scenarios. In contrast, UDC-VIT employs a Quad-Bayer Coding (QBC) camera module from the Samsung Galaxy Z-Fold 5 to more accurately mimic actual noise and transmittance decrease.

✻ 플레어
✻ Flare
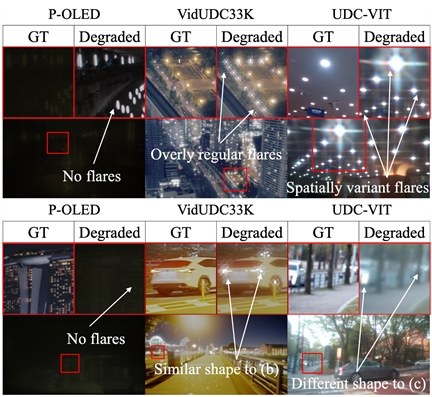
기존 합성 데이터셋은 UDC degradation의 핵심 특징인 영상 내 위치(spatial), 시간(temporal), 그리고 광원(light source) 조건에 따라 변화하는 다양한 flare를 제대로 묘사하지 못하는 한계가 있습니다. UDC-VIT는 이러한 variant flare를 자연스럽고 다양하게 포함하여 실제 환경을 잘 반영합니다.
Previous synthetic datasets fail to capture the critical UDC degradation characteristic of spatially, temporally, and light-source variant flares. UDC-VIT successfully captures these variant flares, providing a more realistic representation of real-world flare phenomena.
✻ 비자연적이고 연구에 덜 유의미한 장면
✻ Less meaningful and strange scenes
PSF convolution 기반으로 제작된 일부 비디오 데이터셋(예: VidUDC33K)은 특정 픽셀 값 이상 영역에 임의로 scaling 후 PSF convolution을 적용하여 flare를 생성하다 보니 비자연스럽고 의미가 떨어지는 장면들이 포함된 경우가 많습니다. 구체적인 예는 아래와 같습니다:
- 케이스 1: 열화된 프레임에 UDC 플레어가 없고, 타겟 영상에서 보이는 일반적인 렌즈 플레어와 유사한 플레어만 나타남
- 케이스 2: 현실적으로 일어나기 어려운 상황에서 플레어 발생
- 케이스 3: 타겟 영상과 열화 영상 모두에 의도하지 않은 흰색 아티팩트가 존재
- 케이스 4: PSF의 동적 변화를 시뮬레이션하는 과정에서 첫 번째 프레임을 제외한 대부분의 프레임이 어두워지고 거의 특징이 없는 영상으로 나타남
- 케이스 5: 일부 영상은 연구에 크게 기여하지 못할 가능성이 있어, 활용 가치에 대한 재고가 필요함
Some PSF convolution-based video datasets (e.g., VidUDC33K) produce unnatural and less meaningful scenes due to the scaling of pixel values before PSF convolution to generate flare. Below are the representative examples:
- Case 1: The degraded frames lack UDC flares, displaying flares resembling typical lens flares seen in the ground truth frame.
- Case 2: Flares appear in improbable situations.
- Case 3: Unintended white artifacts exist both in the ground-truth and degraded videos.
- Case 4: Some videos showcase darkened and nearly featureless, degraded frames, except for the first frame, due to the simulation of the dynamic changes in the PSF.
- Case 5: Some videos may not significantly contribute to research, prompting consideration of their relevance.

This work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) under Grant No. RS-2023-00222663 (Center for Optimizing Hyperscale AI Models and Platforms), and by the Institute for Information and Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) under Grant No. 2018-0-00581 (CUDA Programming Environment for FPGA Clusters) and No. RS-2025-02304554 (Efficient and Scalable Framework for AI Heterogeneous Cluster Systems), all funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea. Additional support was provided by the BK21 Plus Program for Innovative Data Science Talent Education (Department of Data Science, SNU, No. 5199990914569) and the BK21 FOUR Program for Intelligent Computing (Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SNU, No. 4199990214639), both funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) of Korea. This work was also partially supported by the Artificial Intelligence Industrial Convergence Cluster Development Project, funded by the MSIT and Gwangju Metropolitan City. It was also supported in part by Samsung Display Co., Ltd. Research facilities were provided by ICT at Seoul National University.
안규수+‡,
김지수+,
이상익+§,
이현규*,
고병현*,
박찬우*,
이재진*+
* 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학부
+ 서울대학교 데이터사이언스대학원
‡ 삼성디스플레이 연구소
§ 삼성디스플레이 구동개발팀
Kyusu Ahn+‡,
JiSoo Kim+,
Sangik Lee+§,
HyunGyu Lee*,
Byeonghyun Ko*,
Chanwoo Park*,
Jaejin Lee*+
*Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Seoul National
University
+Graduate School of Data Science, Seoul National University
‡ Research Center, Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
§ Mobile Display Electronics Development Team, Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
