UDC-SIT
Under Display Camera(UDC)는 화면 아래에 카메라를 배치해 풀스크린 디스플레이를 구현하는 기술입니다. 그러나 UDC는 저투과율, 블러, 노이즈, 플레어 등 복합적인 이미지 열화(degradation) 문제가 동반되어 이미지 복원이 필수적입니다. UDC-SIT는 이러한 과제를 해결하기 위해 제작된 데이터셋으로, 다양한 환경(주야간, 실내외, 다양한 광원과 플레어 조건)에서 촬영되었습니다.
Under-Display Camera (UDC) is a technology that places the camera beneath the screen, allowing for a full-screen display. However, UDC inevitably causes complex image degradation issues, such as low transmittance, blur, noise, and flare, making image restoration essential. UDC-SIT is a real-world dataset designed to address these challenges by providing paired images captured under diverse conditions, including day and night, indoor and outdoor scenes, and various lighting and flare settings.
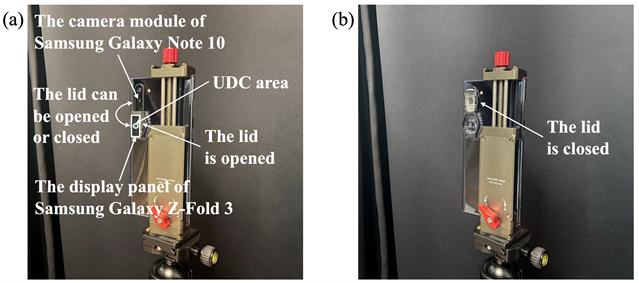
쌍 이미지 간 정밀한 정렬 정확도(alignment accuracy)를 확보하기 위해, 이미지 촬영 시스템을 제안하였고, 고품질 타겟 이미지와 UDC 열화 이미지를 동시에 수집하였습니다.
수집된 이미지 쌍은 이산 푸리에 변환(discrete Fourier transform, DFT)을 활용하여 딥러닝 학습을 위한 쌍 데이터를 97.26%의 높은 정확도로 정렬하였습니다.
기존 연구에서는 합성 이미지에 의존해 왔으나, 본 데이터셋은 최초의 실제 UDC 데이터셋으로서, 복원 모델의 성능을 보다 정확하게 평가할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
To ensure precise alignment accuracy between paired images, a dedicated image acquisition system is developed to capture high-quality target images
and UDC-degraded images simultaneously. The collected pairs are aligned with high precision using the discrete Fourier transform (DFT),
achieving 97.26% alignment accuracy for reliable deep learning training. While previous studies have relied on synthetic images,
this dataset is the first real-world UDC dataset, providing a more accurate benchmark for evaluating the performance of restoration models.
| 데이터셋 이름 | 형태 | 장면 | 데이터셋 개수 | 해상도 | 플레어 존재 여부 | 데이터셋 공개 여부 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-OLED/P-OLED | 이미지 | 합성 | 300 | 1024x2048x3 | ✓ | |
| SYNTH | 이미지 | 합성 | 2,376 | 800x800x3 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pseudo-real | 이미지 | 실제 | 6,747 | 512x512x3 | ✓ | ✓ |
| UDC-SIT | 이미지 | 실제 | 2,340 | 1792x1280x4 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Dataset | Type | Scene | Dataset Size | Resolution | Flare | Publicly Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-OLED/P-OLED | Image | Synthetic | 300 | 1024x2048x3 | ✓ | |
| SYNTH | Image | Synthetic | 2,376 | 800x800x3 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pseudo-real | Image | Real | 6,747 | 512x512x3 | ✓ | ✓ |
| UDC-SIT | Image | Real | 2,340 | 1792x1280x4 | ✓ | ✓ |
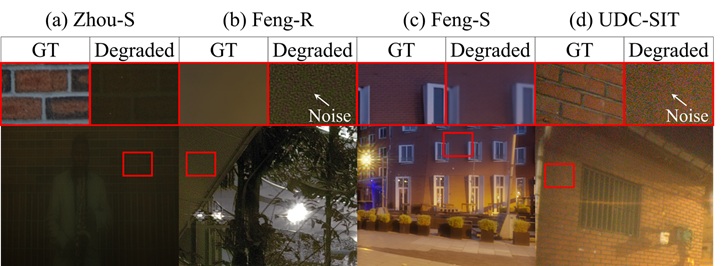
✻ 노이즈 및 투과율 감소
✻ Noise and Transmittance Decrease
기존 합성 데이터셋은 실제 UDC의 심각한 노이즈와 투과율 저하를 충분히 반영하지 못하며, 현실감이 떨어집니다. UDC-SIT는 실제 이미지를 촬영하여 실제의 열화를 가장 잘 반영합니다.
Existing synthetic datasets fail to adequately capture the noise and decrease in transmittance of real-world UDC images. In contrast, UDC-SIT captures these degradations most accurately since it captures actual scenes.
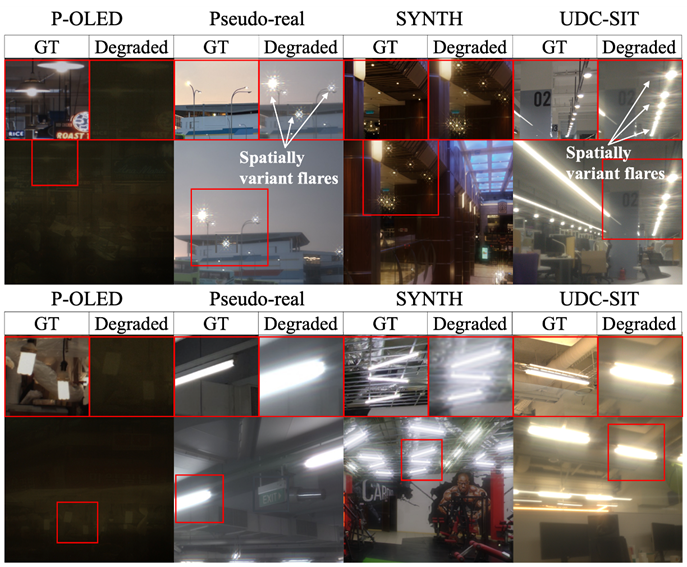
✻ 플레어
✻ Flare
합성 데이터셋은 플레어 패턴이 단순하거나 제한적이지만, UDC-SIT는 다양한 강도 및 위치별로 상이한(spatially variant) 플레어와 조명 조건(실내·실외, 주야간)을 포함합니다.
Synthetic datasets often contain only simple or limited flare patterns. In contrast, UDC-SIT encompasses spatially variant flares of varying intensities and positions, as well as diverse lighting conditions (indoor/outdoor and day/night).
✻ 가림 현상(Occlusion)
✻ Occlusion
기존의 의사 실제(pseudo-real) 데이터셋은 딥러닝 모델을 이용해 정렬하는 과정에서 아티팩트(artifact)가 발생해 가림 현상이 생기지만, UDC-SIT는 DFT 기반으로 정렬하여 이러한 왜곡이 없습니다.
Existing pseudo-real datasets rely on deep learning models for alignment, which introduces artifacts that cause occlusion effects. In contrast, UDC-SIT uses DFT-based alignment to avoid such distortions.

This work was supported in part by the Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant (No. 2018-0-00581, CUDA Programming Environment for FPGA Clusters) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00222663). This work was also supported in part by the Samsung Display Co., Ltd. ICT at Seoul National University provided research facilities for this study.
안규수+‡,
고병현*,
이현규*,
박찬우*,
김우진+,
이규성+,
이동영+,
임상수+,
최광호+,
조경제+,
소연경+,
석지헌+,
이재환*,
최동훈*,
박대영*,
이재진*+
* 서울대학교 컴퓨터공학부
+ 서울대학교 데이터사이언스대학원
‡ 삼성디스플레이 연구소
Kyusu Ahn+‡,
Byeonghyun Ko*,
HyunGyu Lee*,
Chanwoo Park*,
Woojin Kim+,
Gyuseong Lee+,
Dongyoung Lee+,
Sangsoo Im+,
Gwangho Choi+,
Gyeongje Jo+,
Yeonkyoung So+,
Jiheon Seok+,
Jaehwan Lee*,
Donghun Choi*,
Daeyoung Park*,
Jaejin Lee*+
*Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Seoul National
University
+Graduate School of Data Science, Seoul National University
‡ Research Center, Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
